Breath Senses Health!
We are on a breath of fresh air mission, crafting clever devices that help hospitals and clinics pinpoint respiratory ailments with a puff of diagnostic genius!
At Sunvou, we pride ourselves on being the premier manufacturer of advanced breath test medical devices, enabling tailored diagnoses and treatments for patients worldwide. Our commitment to innovation and quality positions us at the forefront of this vital healthcare sector.
Sunvou FeNO 1+2 All-in-One
Extended Diagnosis of Various Types of Respiratory Inflammation and Comorbidities of Asthma
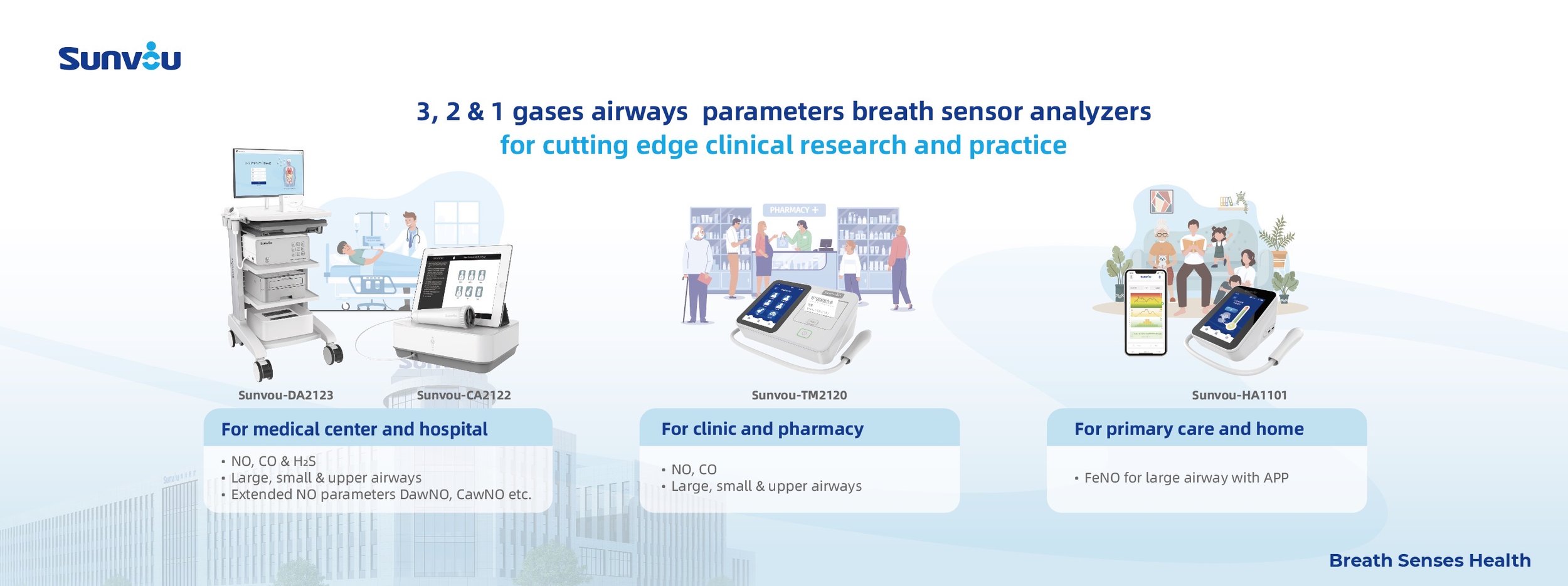
Bronchial FeNO: Large Airway Inflammation via FeNO50
Alveolar FeNO: Small Airway Inflammation via CaNO (FeNO200) - Medication Adjustment to Ultrafine Particle ICS
Nasal FnNO : Upper Airway Inflammation via FnNO (FeNO10) - Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis: Medication Adjustment to Nasal ICS.
New SIBO Device by Sunvou!
SIBO All-in-One
5 Diagnostic Biomarkers in Human Breath all-in-one Device
Biomarkers: H2 + CH4 + H2S + NO + CO for the Diagnostics of:
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Colorectal Cancer
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Microbiota Changes
Inflammated Bowel Sickness
-
When bacteria in the small intestine ferment carbohydrates, they produce hydrogen gas. Elevated levels of hydrogen in the breath after ingestion of a test sugar solution (usually glucose or lactulose) indicate that bacteria are fermenting the sugar in the small intestine, suggesting the presence of SIBO.
-
Some types of bacteria in the gut can convert hydrogen into methane. High levels of methane in the breath are associated with constipation-predominant symptoms and have been linked to a specific form of bacterial overgrowth involving methanogenic archaea. Methane production is particularly associated with slower transit times through the intestines.
-
Detects Sulfur-Reducing Bacteria: H2S is produced by sulfur-reducing bacteria in the gut. Elevated levels may indicate an overgrowth of these bacteria, which are not detected by standard hydrogen (H2) or methane (CH4) measurements.
-
Indicates Inflammatory Activity: NO is a marker of inflammation in the gut. Elevated NO levels can indicate inflammation or immune responses that may be associated with bacterial overgrowth or other gastrointestinal conditions.
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
-

Use of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide to Guide the Treatment of Asthma An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline
Conclusions: Clinicians should consider this recommendation to measure FENO in patients with asthma in whom treatment is being considered based on current best available evidence.
-

A European Respiratory Society technical standard: exhaled biomarkers in lung disease
The most important advantage of modelling NO dynamics is the gain of CANO that may be useful in assessing inflammation in small airways or lung parenchyma both in airway diseases and interstitial lung diseases.
-

Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurement in Clinical Asthma Management
This review discusses the clinical application of FENO measurement in asthma care, from diagnosis to treatment se- lection, and describes its place in current international expert guidelines.
-

Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma
Type 2 inflammation in asthma is generally suppressed by glucocorticoids, as evidenced by a rapid decrease in Feno (mediated by airway in- terleukin-13) when treatment with inhaled gluco- corticoids is initiated and an immediate decrease in blood eosinophil counts (mediated by sys- temic interleukin-5) with the use of oral gluco- corticoids.
-

European position paper on diagnostic tools in rhinology
Nasal NO is a sensitive and specific test for PCD in cooperative patients (generally over five years old) with a high clinical suspicion for this disease. To a lesser extent it may also be a useful adjunct in a potential diagnosis of CF.
-

Cough Hypersensitivity and Chronic Cough
Measurement of markers of type 2 inflammation, such as fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) or sputum eosin- ophil count, may be useful in the early stage of work-ups of patients with chronic cough.
Catalogues
-

Sunvou FeNO 1+2
-

Sunvou & Others
-

Result Interpretation
-

SIBO: Exhaled H2, CH4, NO, CO & H2S
-

Clinical Applications of SIBO
-

SIBO Biomarkers
Sunvou Europe & Middle East
Contact us.
Sunvou EU - Europe & Middle East
int@sunvou.com
ulasatalay@sunvou.com
+90 (533) 965-7532
Besiktas, Istanbul 34349



